

One of the ratios, which is known as the capital turnover ratio, is used for measuring the company’s performance.Įspecially it stands helpful in the manufacturing industry, which is also known as the capital-intensive industry.įairly it is way simpler to calculate the Fixed Asset Turnover ratio.
This helps them by allowing them to perform based on an assessment only on openly available information provided by the company. This led lenders and investors to often rely on the company’s financial ratios and company’s financial statement reports. It can be either audited or even not is depends on the company. On the other hand, shareholders from outside and investors often have only the financial statements. The ratio is also sometimes known as the fixed asset ratio.When we talk about improvement or prediction of a company’s performance, then a lot of unique insight is needed by the leadership team.Īs the leadership team has access to all kind of financial reports and data which are not shared with the outside world. The fixed asset turnover ratio is similar to the tangible asset ratio, which does not include the net cost of intangible assets in the denominator. Thus, a business whose management team deliberately decides not to re-invest in its fixed assets will experience a gradual improvement in its fixed asset ratio for a period of time, after which its decrepit asset base will be unable to manufacture goods in an efficient manner.

Ongoing depreciation will inevitably reduce the amount of the denominator, so the turnover ratio will rise over time, unless the company is investing an equivalent amount in new fixed assets to replace older ones. Accelerated DepreciationĪ potential problem with this ratio may arise if a company uses accelerated depreciation, such as the double declining balance method, since this artificially reduces the amount of net fixed assets in the denominator of the calculation and makes turnover appear higher than it really should be.
#Fixed asset turnover interpretation software
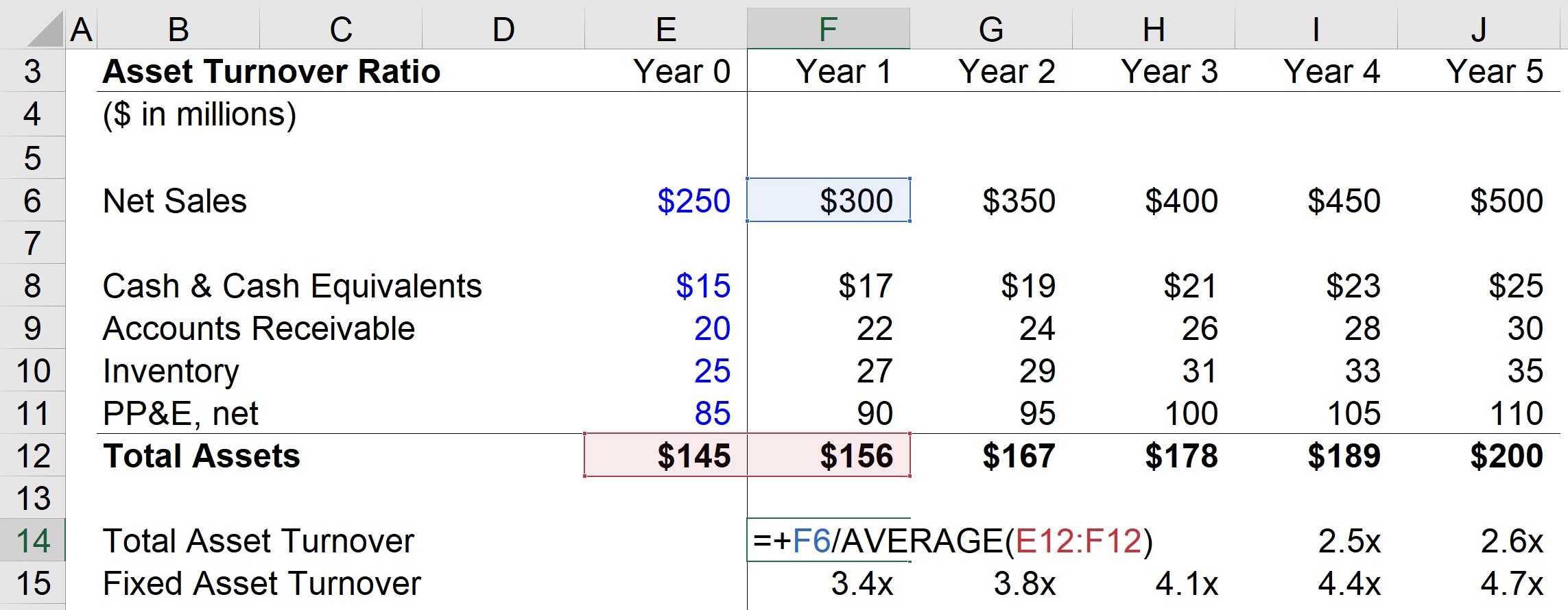
In other industries, such as software development, the fixed asset investment is so meager that the ratio is not of much use. The fixed asset turnover ratio is most useful in a "heavy industry," such as automobile manufacturing, where a large capital investment is required in order to do business. Several cautions regarding the use of this measurement are noted below. = 3.0 Turnover per year Problems with the Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio The calculation of ABC's fixed asset turnover ratio is: Sales over the last 12 months totaled $9,000,000. Net annual sales ÷ (Gross fixed assets - Accumulated depreciation) = Fixed asset turnover ratio Example of the Fixed Asset Turnover RatioĪBC Company has gross fixed assets of $5,000,000 and accumulated depreciation of $2,000,000. Do not include intangible assets in the denominator, since it can skew the results. It may be necessary to obtain an average fixed asset figure, if the amount varies significantly over time. The formula for the ratio is to subtract accumulated depreciation from gross fixed assets, and divide that amount into net annual sales.
#Fixed asset turnover interpretation how to
How to Calculate the Fixed Asset Turnover Ratio A corporate insider has access to more detailed information about the usage of specific fixed assets, and so would be less inclined to employ this ratio. The concept of the fixed asset turnover ratio is most useful to an outside observer, who wants to know how well a business is employing its assets to generate sales.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
